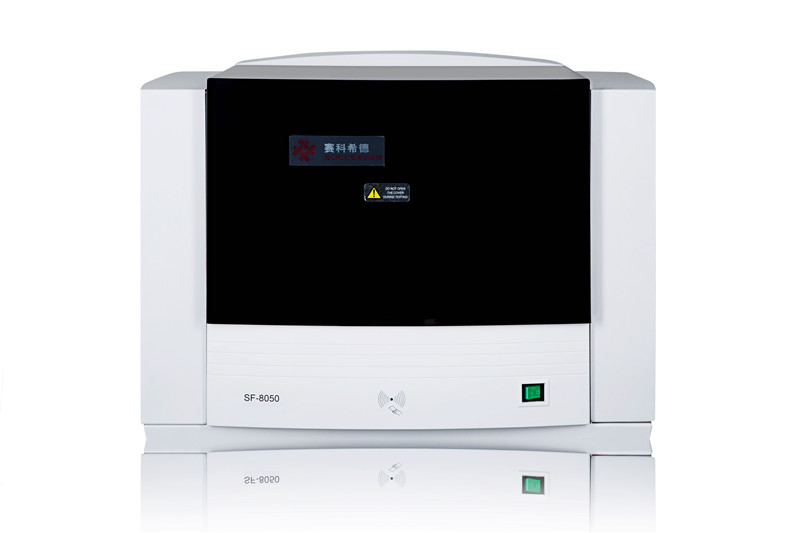
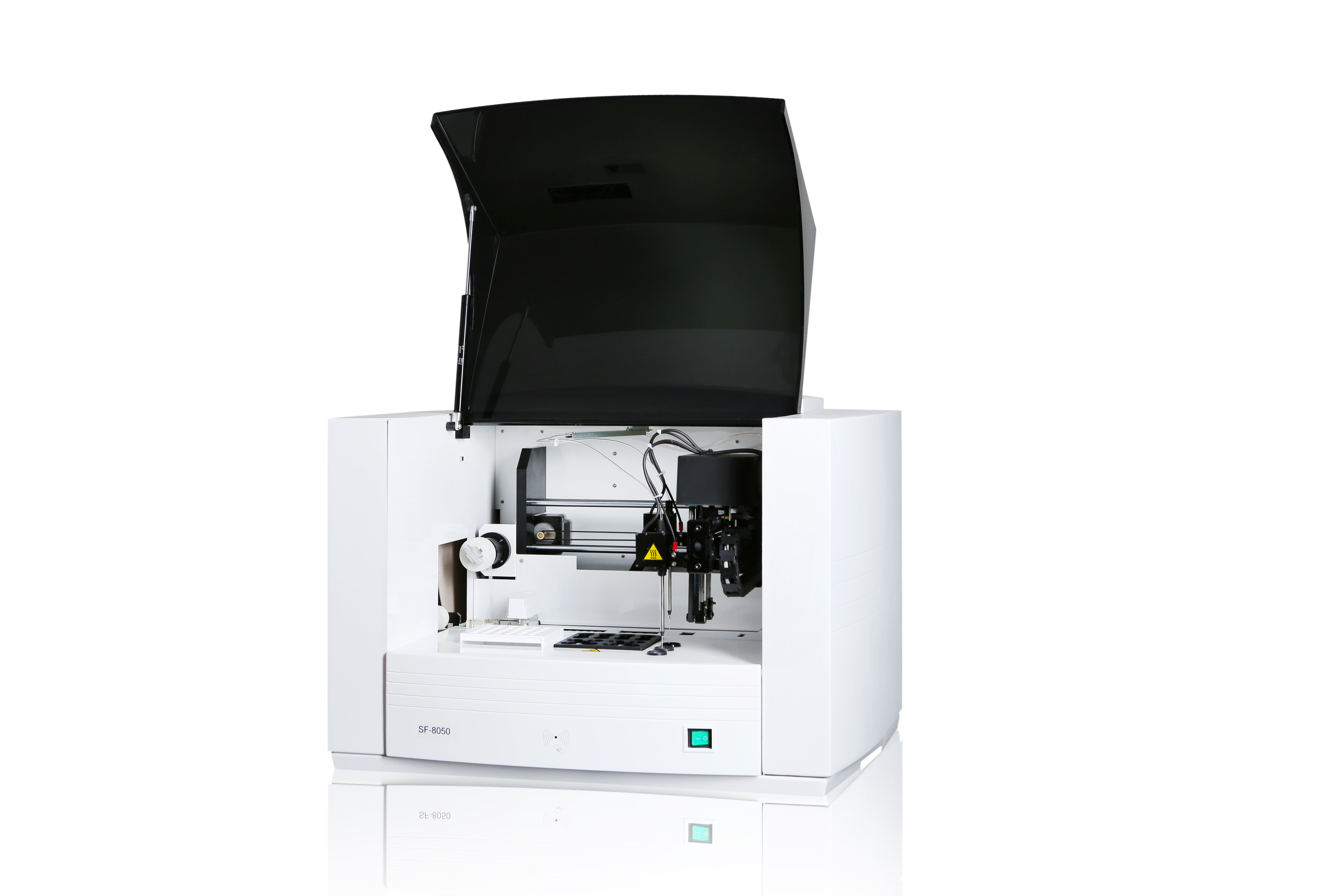
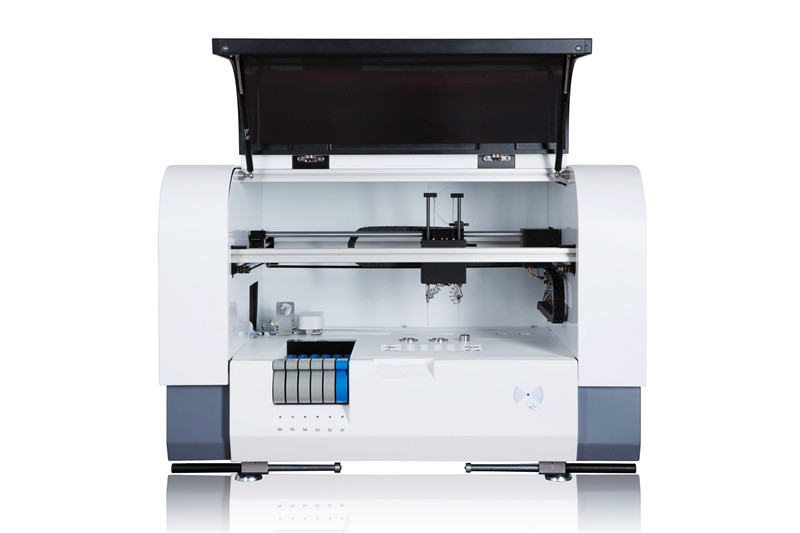
working principle
1. Coagulation method: adopts double magnetic circuit magnetic bead coagulation method, which is carried out on the basis of the continuous increase of the measured plasma viscosity.
The movement of the bottom of the measuring cup along a curved track detects an increase in plasma viscosity. Independent coils on both sides of the detection cup produce opposite electromagnetic field drives moving magnetic beads movement. When plasma does not undergo a coagulation reaction, the viscosity does not change, and the magnetic beads oscillate with a constant amplitude. When the plasma coagulation reaction occurs. Fibrin is formed, the plasma viscosity increases, and the amplitude of the magnetic beads decays. This amplitude change is calculated by mathematical algorithms to get the solidification time.
2.Chromogenic substrate method: artificially synthesized chromogenic substrate, which contains the active cleavage site of a certain enzyme and color-producing substance, which remains after being activated by the enzyme in the test specimen or the enzyme inhibitor in the reagent interacts with the enzyme in the reagent The enzyme cleaves the chromogenic substrate, the chromogenic substance is dissociated, and the color of the test specimen changes, and the enzyme activity is calculated based on the change in absorbance.
3. Immunoturbidimetric method: The monoclonal antibody of the substance to be tested is coated on the latex particles. When the sample contains the antigen of the substance to be tested, an antigen-antibody reaction occurs. A monoclonal antibody can trigger an agglutination reaction, leading to a corresponding increase in turbidity. Calculate the content of the substance to be tested in the corresponding specimen according to the change in absorbance

 Login/Register
Login/Register














 Business card
Business card Chinese WeChat
Chinese WeChat English WeChat
English WeChat